Data model design
A well-designed data model has the benefit of reusability, extensibility through specialization, and easy maintainability. Data model design is equally as important to a software project as a process design.
The data model provides a good blueprint of the complete data flowing in the life cycle of the business processes. A good blueprint of the data helps to utilize the data perfectly and efficiently.
When you begin designing the data model solution for the given business scenario, the basic steps of data modeling are:
- Identify data objects.
- Identify attributes for each data object.
- Identify existing data objects that can be reused (inheritance or composition).
- Relate data objects.
- Plan for the persistence/integration of the data objects created by the application.
Data model design is a very important and critical phase in the application development to meet the business needs. A lead system architect (LSA) focuses on data modeling to use the following benefits.
- The complexity of the data can be reduced by classifying and modeling the data.
- With data modeling, the required data can be identified to meet the business requirements; plans can be made to capture the data from the source and avoid any loss of data.
- Data modeling helps in designing a save plan so that all the captured data is persisted and the integrity of the system is maintained.
- The accuracy and correctness of data can be maintained by considering the data integrity designs (maintaining the single source of truth).
- Backup of data and publishing of data to other parties can be properly planned in data modeling.
- Data modeling helps to define and describe the data as required by the different stakeholders. For example, a manager may need data for reporting, but the developer uses the same data to execute some business logic.
- Future requirements will be considered in data modeling hence application remains robust, flexible, and scalable.
To realize the benefits of the data model, consider the following example. A Purchase Request application has two different processes: Order Management and Product Management. Two sprint teams are implementing Order Management and Product Management at the same time, each modeling their own definition of a product. There is a risk that the two sprint teams may deliver two distinct designs for a product instead of one enterprise-wide, reusable definition. This situation results in having different ways to detect the same product and is a duplication of data. The consequences are heavy maintenance, less flexible application, and non-scalable application.
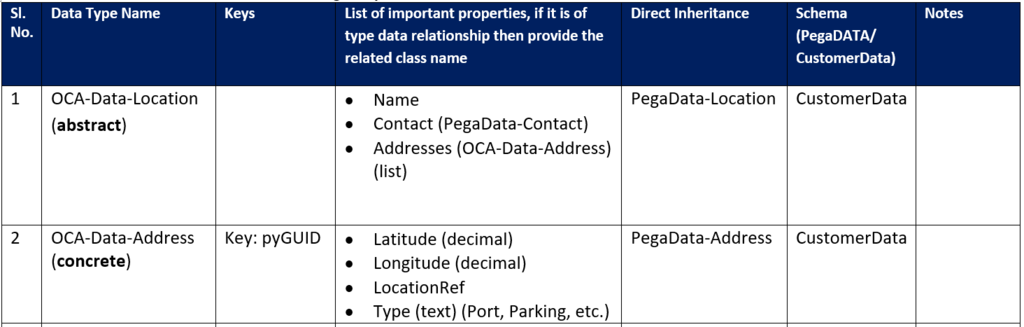
Note: If a data element already exists, consider how it fits into your requirements. For example, when there is an 80 percent fit between a Pega class and the required business object, then use the out-of-the-box data elements. Explore PegaData-* and check if you can reuse compose-with, and inherit-from these classes. Otherwise, plan to create new data elements.
Data model design discusses organizing and designing the data but not the operations performed on the data. The case type is different than the data it contains. Case type performs operations on the data. One of the primary purposes of a case is to manage the data required to complete one micro journey or a single business transaction. The primary purpose of data is to compose other data types or used by one or more case types.
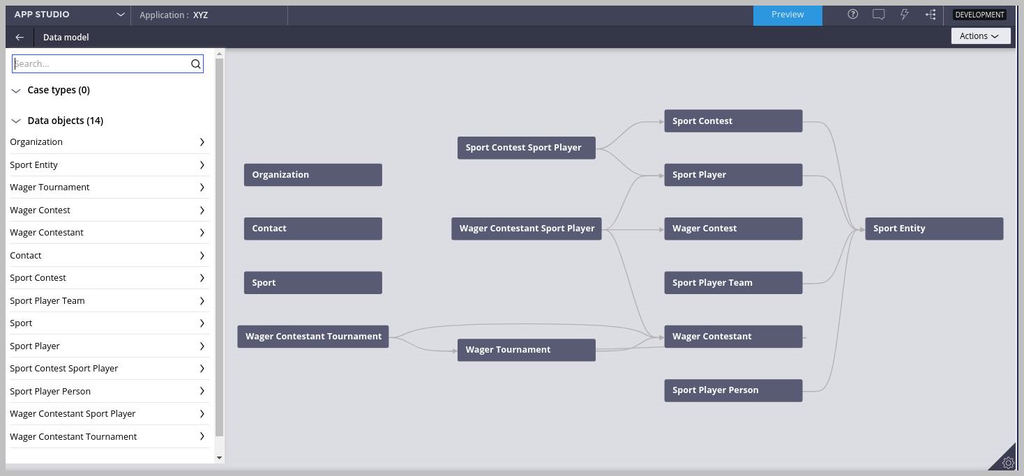
At the end of the data modeling, it is a good idea to represent data and their relationship with a relation diagram. App Studio creates this relationship diagram, so it is unnecessary to use third-party tools to draw the data relationship diagram. At the design phase (before actual implementation in Pega), you can use simple boxes and connectors to represent the data modeling for easy understanding.
This Topic is available in the following Module:
If you are having problems with your training, please review the Pega Academy Support FAQs.
Want to help us improve this content?