Pega Process AI overview
Introduction
In recent years, artificial intelligence has moved out of the labs and helped enterprises generate proven business value. At the same time, operationalizing AI can be a bottleneck. Pega Process AI™ tackles this problem by using AI to self-optimize processes and applying your own AI in Pega case management.
Video
Transcript
This video provides an overview of the Pega Process AI capabilities in intelligent automation.
Process management aims to optimize business processes by increasing efficiency, consistency, and transparency, which decreases costs and improves quality.
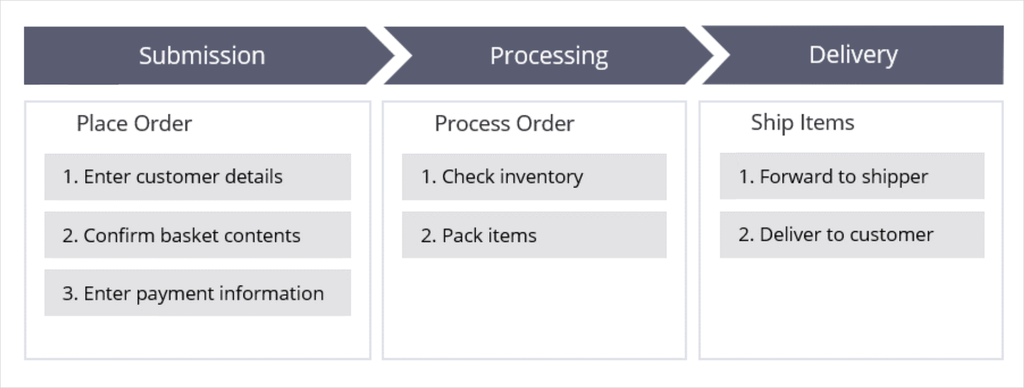
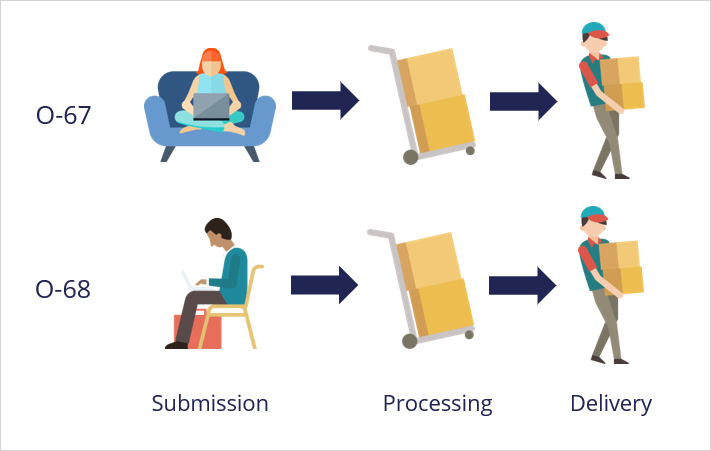
For example, consider an online order process. The customer submits an order, and the company processes and then delivers the order.
An Pega Platform application that models the online order process follows the same sequence as a series of stages. A case type is the abstract model of that process.
Case types model repeatable business transactions that might refer to a customer, or another entity, such as a machine in a maintenance case type.
The case life cycle for a case type helps to visualize the work to complete as part of a business transaction.
Each stage in the life cycle contains the steps required to complete it and move to the next stage.
A case is a specific transaction instance of the case type.
Each time a user submits an online order, Pega Platform creates an order case and assigns the case a unique identifier.
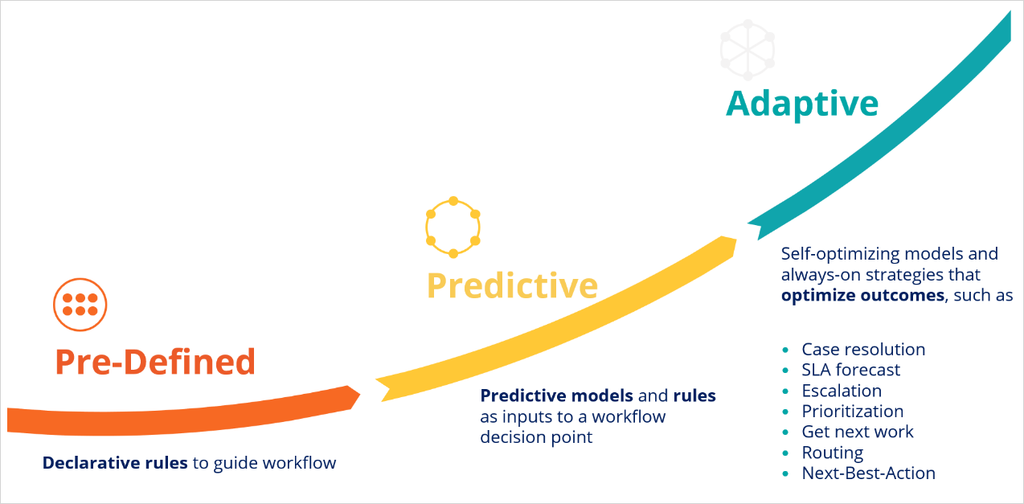
A case type can use declarative rules to manage the workflow, for example, to confirm that the order contains a valid shipping address or the order amount threshold to qualify for free shipping.
Pega Process AI can improve the quality of the decisions in the workflow by weighting in predictions, driven by predictive models.
The first approach is to operationalize existing predictive models that have proven their efficiency, to support the decisions that benefit from predictions, such as credit risk in a sales case or fraud risk in a claims case.
For example, the decision not to process an order can be based on a high credit risk score, and then the application can route the dubious claim for closer inspection.
The inputs for such a predictive model can be attributes of the case itself, such as the claimed amount in a claims case type, but they can also include data such as the number of claims submitted recently by the same customer.
You can build predictive models in Prediction Studio, import the models in the PMML and H2O formats, or run externally on the Amazon SageMaker and Google ML platforms to drive a prediction.
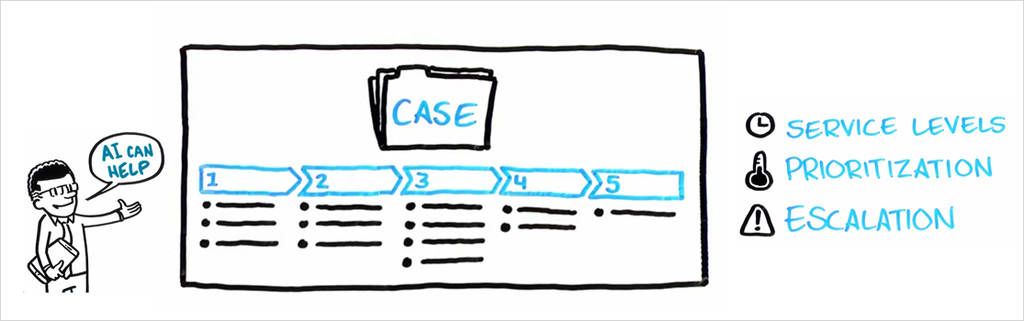
To optimize case outcomes, use adaptive models that can predict outcomes, such as case resolution, or intelligently prioritize and route cases to optimize business value and customer experience.
Adaptive models self-optimize by learning from the previous case outcomes that they capture.
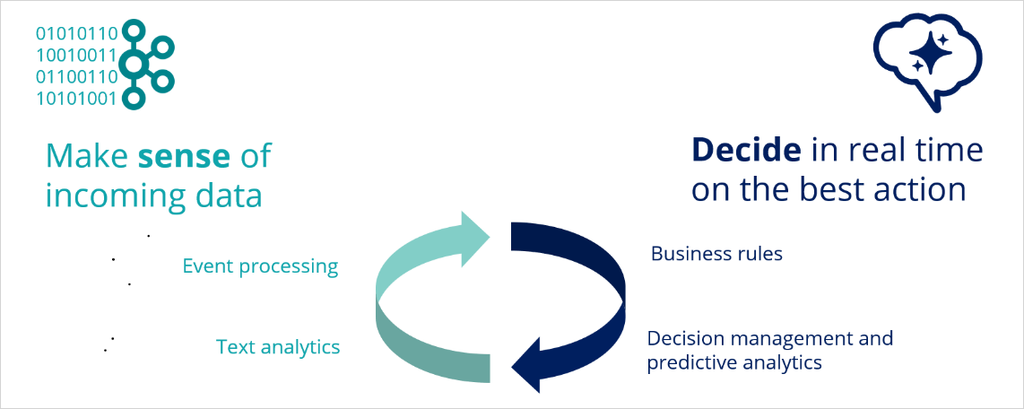
The objective of Pega Process AI is to make sense of the incoming data and then decide on the best action to take in a specific stage of the case.
You can enhance the incoming data analysis by event processing to detect patterns of interest in real-time data streams and by natural language processing of incoming text.
The decision is based on the business rules and supported by predictive analytics. This process is repeated every time that the case requests a decision.
As the number of processed cases increases and model evidence accumulates, the predictive power of the models increases over time.
To summarize, Pega Process AI uses artificial intelligence in case management to produce better business outcomes.
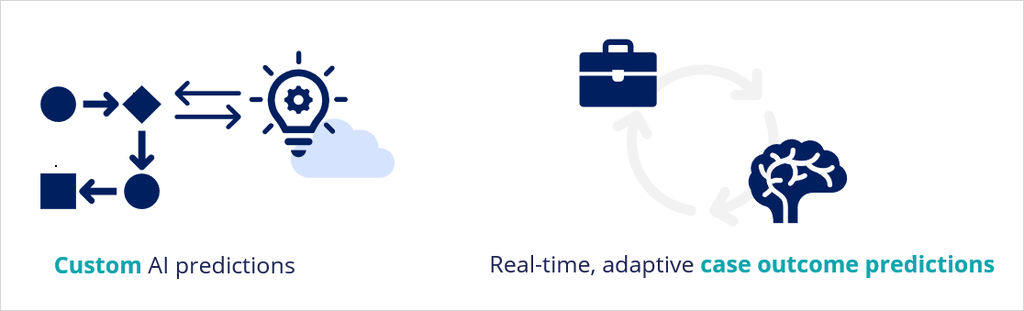
You can use real-time, adaptive case outcome predictions and your own AI models in custom predictions.
This Topic is available in the following Modules:
If you are having problems with your training, please review the Pega Academy Support FAQs.
Want to help us improve this content?