Circumstance Rules
Circumstance rules
Circumstancing establishes a baseline for expected case behavior and adds variants to address exceptions to the behavior. The goal of circumstancing is to create a variant for each anticipated situation. Pega selects the appropriate variant, or circumstance, to use based on the details of the case.
When you circumstance a rule, you create a set of focused rules to address exceptions to case processing, rather than one all-encompassing rule. Since each rule focuses on a specific exception, application maintenance and updates are easier and can be delegated to business users. Reusing the rules you create at the application or enterprise level is also easier.
How to circumstance a rule
To circumstance a rule, you start by creating a base rule to define the expected behavior. Pega uses the base rule unless a circumstanced version is more appropriate.
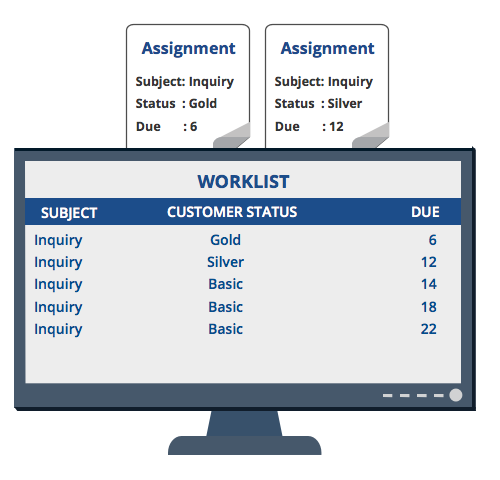
Consider a company with different response time obligations for elite and non-elite customers. The response time for non-elite customers is the expected behavior. In this situation, the response-time goal is 24 hours. So you create a base rule—in this case, a service level—to enforce the response time goal for non-elite customers.
Then, you identify any exceptions to the expected behavior. For each exception, you circumstance the base rule to address the difference from the expected behavior. For example, elite customers with silver status have a response time goal of 12 hours. You circumstance the base rule to enforce the response time goal for customers with silver status. You can then create another circumstance to address the goal time for customers with gold status, who have a service level response goal of six hours.
Types of circumstancing conditions
You can circumstance a rule according to the value of one or more conditions. You define a condition based on one variable, multiple variables, or the processing date, then apply the condition to a variant of the rule. When using the rule, the application evaluates the conditions defined on all the circumstanced variants. If one of the circumstancing conditions is satisfied, the application uses the corresponding rule variant. Otherwise, the application uses the base rule.
Pega supports the following types of circumstance conditions.
-
Single value – the rule variant is effective whenever the value of a single property satisfies the circumstancing condition. You specify the property to evaluate a comparison value when circumstancing a rule. If the value of the property matches the specified value for a case, the application applies the circumstanced variant of the rule, rather than the base rule.
-
Multiple value – the rule variant is effective whenever a combination of property values satisfies the circumstancing condition. Multiple value circumstances are based on a circumstance template and circumstance definition. The circumstance template defines the properties on which to circumstance a rule. The circumstance definition defines the combination of conditions in which a property uses a variant of a rule. You apply the circumstance template and circumstance definition to the rule variant. If the case matches a combination in the circumstance definition, the application uses the circumstanced variant of the rule, rather than the base rule.
-
Date property – the rule variant is effective whenever the value of a date property satisfies the circumstancing condition. This condition can be either a single date or a range of dates. If the value of the property is later than the specified date or falls within the range of dates, the application uses the circumstanced variant of the rule, rather than the base rule.
-
As-of date – the rule variant is effective after a certain date, or during a range of dates. After the specified date or during the specified range, the application applies the circumstanced variant of the rule, rather than the base rule.
Examples of circumstancing conditions
The following video provides examples of each type of circumstancing condition.
Each variant of a rule applies one type of circumstancing condition, though you can combine conditions to circumstance a rule.