Contact policy types
Types of constraints
Too many contact attempts over a short period of time can have a negative impact on a customer's attitude toward further actions by your company. To maximize the lifetime value of every customer relationship, organizations must prevent outreach fatigue by optimizing the number of actions taken.
In Pega Customer Decision Hub™, there are two types of contact limits that allow you to limit actions over a given period of time.
- Customer contact limits
- Suppression policies
Customer contact limits
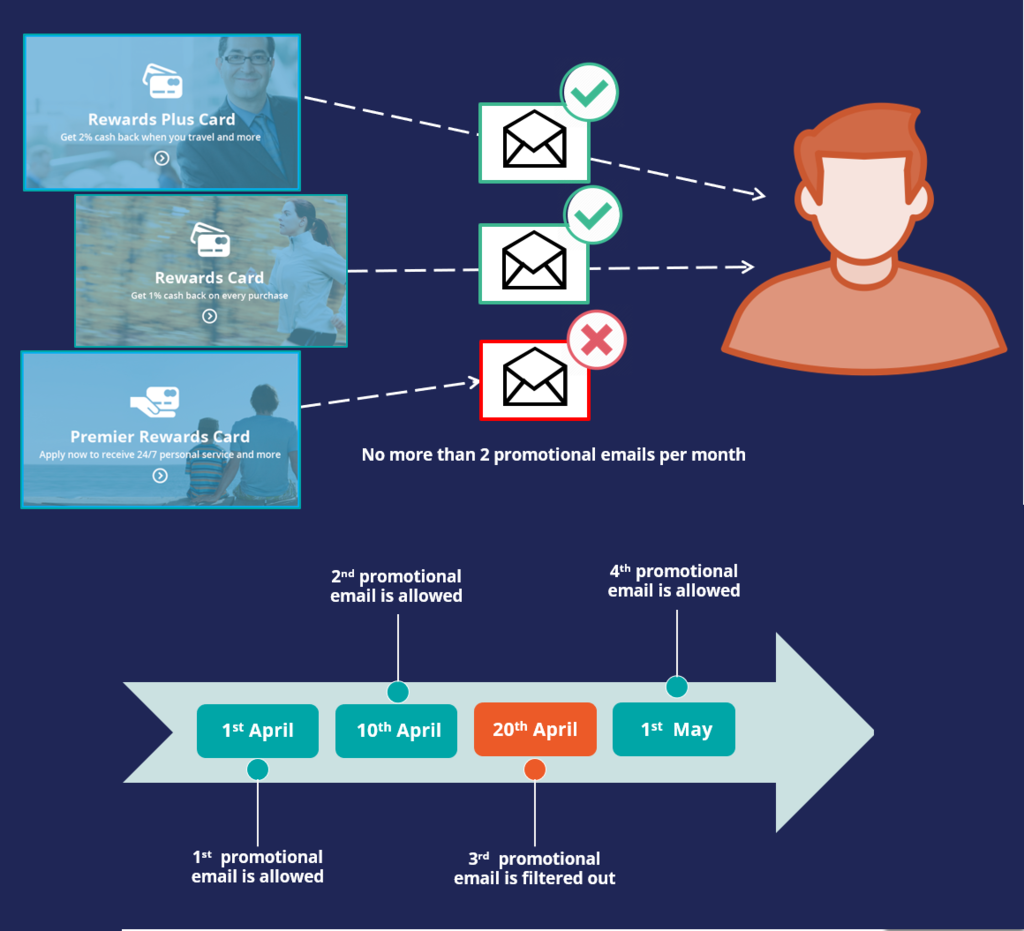
Customer contact limits allow you to limit the number of actions that a customer can receive over a given period of time on a specific channel. These customer contact limits prevent an action from reaching a customer on a specific channel, irrespective of past responses to that action by the customer.
For example, you can decide that you do not want your customers to receive more than two promotional emails per month.
Suppression policies
Suppression policies determine when and for how long an action or group of actions should not be shown to a customer. These suppression policies put an action on hold after a specific number of outcomes are recorded for some or all channels.
Suppressing or pausing an action prevents oversaturation by limiting the number of times a customer is exposed to the same action.
For example, if a customer ignores a credit card promotional offer email twice in the previous 30 days, then the same credit card offer should not be sent to the customer again for the next 60 days.
This Topic is available in the following Modules:
If you are having problems with your training, please review the Pega Academy Support FAQs.
Want to help us improve this content?

