Pega Robotic Automation architecture
Pega Robotic Automation provides two modes of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automation:
- Attended
- Unattended
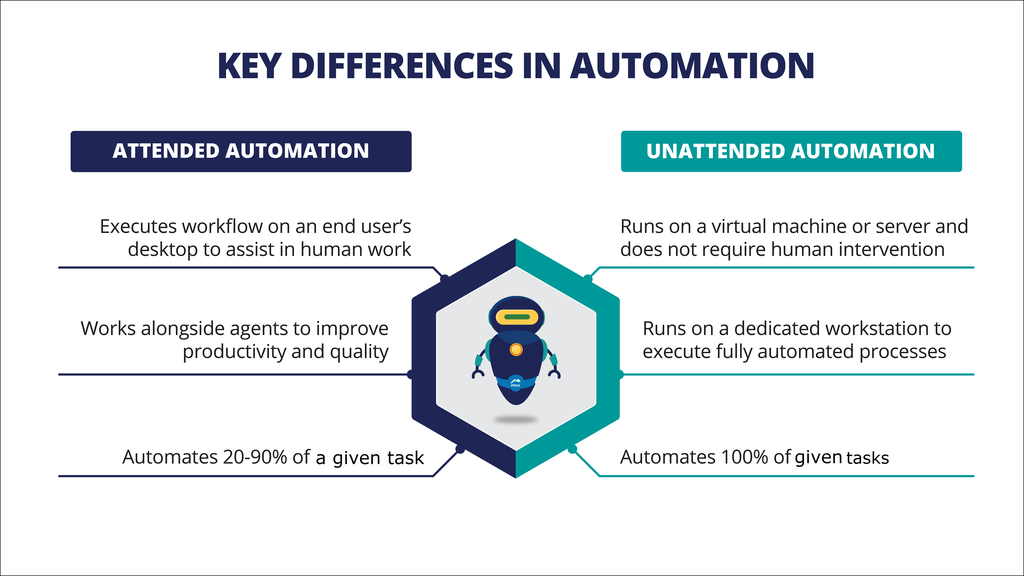
An attended automation assists an agent in handling simple, repetitive tasks. In contrast, an unattended automation automates specific tasks or steps in a Pega Platform™ case type definition, including automated business tasks.
Automation development
When using Pega Robot Studio™ and Pega Robot Runtime™ together, you can test and debug a robotic automation project locally before packaging any deployment. After Pega Robot Studio is installed, Pega Robot Runtime™ is also installed automatically to allow the developer to test and debug the robotic automation project locally before packaging any deployment. Developers need access to all the necessary applications used in the robotic project on their workstation to test and debug it before deployment.
Deployment strategy
A deployment strategy is a process that delivers an automation package from Pega Robot Studio to an attended or unattended robot desktop. The preferred deployment approach for a robotic project is Pega Robot Manager™. Pega Robot Manager is a web-based control management product that provides access to deliver the project to users and robots. Pega Robot Manager provides dashboards and tools to monitor robots to prioritize, reroute, and schedule work.
Runtime Automation desktop
A Robot Runtime workstation runs an automation package on a user or robot machine containing Pega Robot Runtime installed to access application references in the robotic project. Attended and unattended Robotic Processing Automation (RPA) sessions have the same Pega Robot Runtime and application requirements for a runtime workstation.
This Topic is available in the following Modules:
If you are having problems with your training, please review the Pega Academy Support FAQs.
Want to help us improve this content?
