Action arbitration
Introduction
Pega Customer Decision Hub combines analytics, business rules, customer data, and data collected during each customer interaction to create a set of actionable insights that it uses to make intelligent decisions. Arbitration aims to balance customer relevance with business priorities by weighing numerical values for the following factors: propensity, context weighting, action value, and business levers. Learn to create a simple formula for arriving at a prioritization value, which is used to select the top actions.
Video
Transcript
This video explains the concept of action arbitration.
Pega Customer Decision Hub™ combines analytics, business rules, customer data, and data collected during each customer interaction to create a set of actionable insights that it uses to make intelligent decisions. These decisions are known as Next-Best-Action.
Every Next-Best-Action weighs customer needs against business objectives to optimize decisions based on priorities set by the business manager.
U+ Bank, a retail bank, has several actions for its customers and has configured engagement policies to suit both customer needs and business objectives.
In this scenario, a marketer for U+ has designed 200 actions that can be presented to customers. To select the Next-Best-Actions from these, Pega Customer Decision Hub first checks the eligibility conditions and filters the actions. Then, the applicability conditions are run to filter it further. Next, Customer Decision Hub checks the suitability conditions to derive the final set of available actions.
These actions move through one final stage before being presented to customers: the arbitration stage. Arbitration is used to prioritize and choose the best actions based on what is relevant for the customer right now.
Arbitration aims to balance customer relevance with business priorities. The factors weighed are Propensity, Context Weighting, Action Value, and Business Levers, each represented by numerical values. A simple formula is used to arrive at a prioritization value, which is used to select the top actions. The number of top actions selected depends on the channel of interaction. For example, the top three actions, plus two tiles and one hero treatment, can be selected for display on a bank’s website.
Propensity is the likelihood of a customer responding positively to an action; this is calculated by AI. For example, the higher the likelihood of a customer accepting an offer, the higher the Propensity value for that offer.
Context Weighting allows Pega Customer Decision Hub to consider the situational context for each action. For example, if a customer contacts the bank to close their account, the highest-priority action is to ensure that the customer is retained. The priority of an action is increased by a specified value when the context is detected.
Action Value enables you to assign a financial value to an action and prioritize high-value actions over low-value ones. This value is typically normalized across Issues and Groups. For example, an unlimited data plan is more profitable than a limited data plan. So, in a situation where a customer is eligible for both plans, the unlimited plan has higher priority.
Business Levers allow the business to assert some level of control over the prioritization of actions defined within the system. Levers are used to manually nudge Customer Decision Hub toward Next-Best-Actions based on external factors. For example, the recommended Next- Best-Action might be to offer a credit card to a customer when they visit the home page. But to meet a business goal, the Mortgage Line of Business favors a mortgage offer even if that offer is ranked a little lower on the list of possible actions.
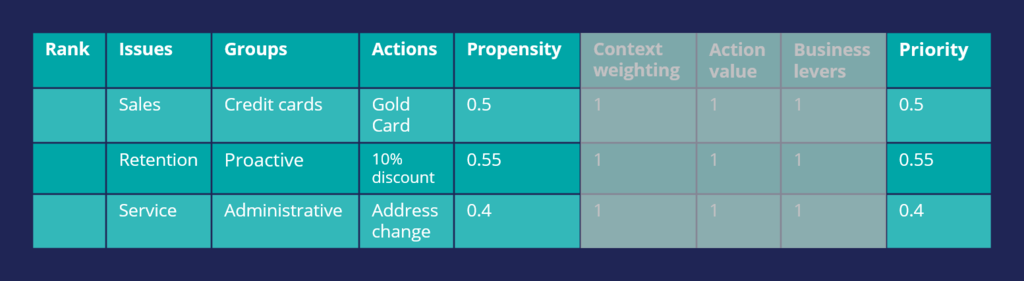
Consider an example where three actions are selected for arbitration. At the moment, only the Propensity is used for prioritization.
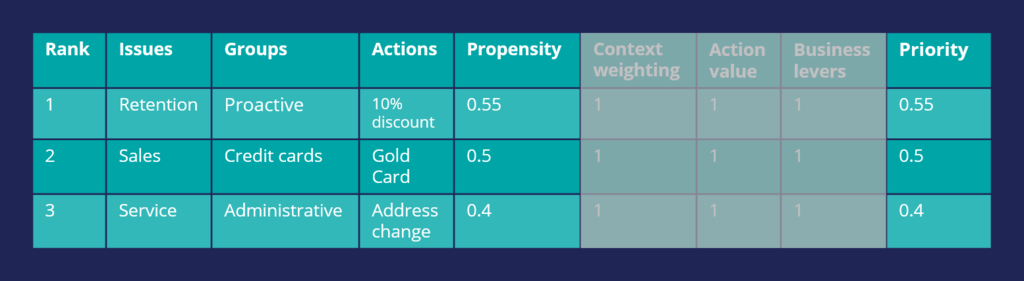
The result of the arbitration is that the top action is the one with the highest Propensity.
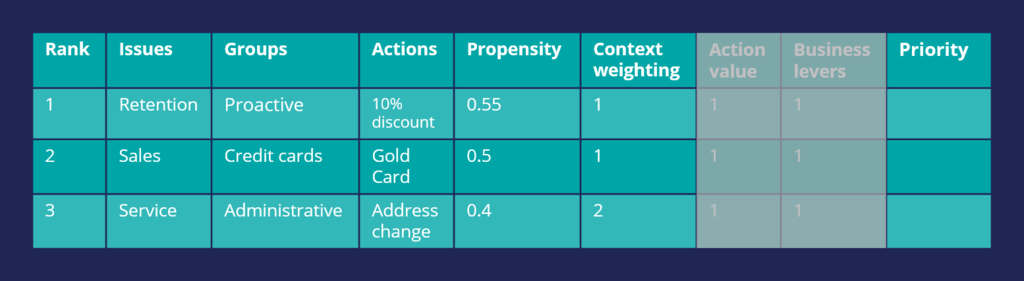
Examine what happens when Context Weighting together with Propensity are considered for arbitration. For example, if the intent of a customer calling customer service is to change their address, the Context Weight of a Service action increases.
As a result, the Arbitration caters to the current need of the customer and presents a Service action as the top action for the customer. Thus, the Arbitration caters to the current need of the customer and presents a Service action as the top action for the customer.
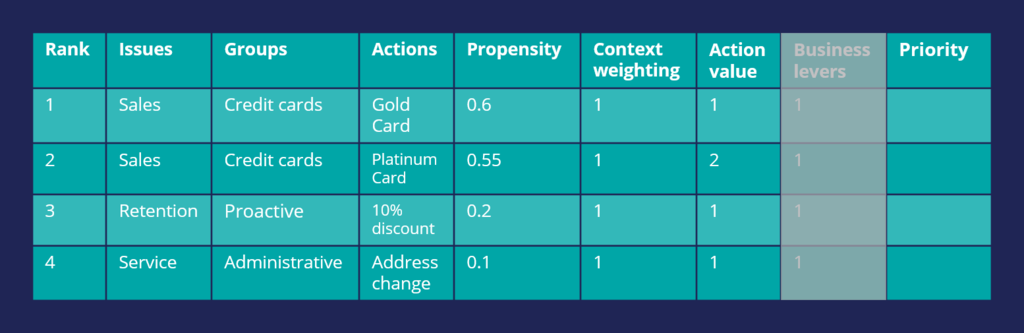
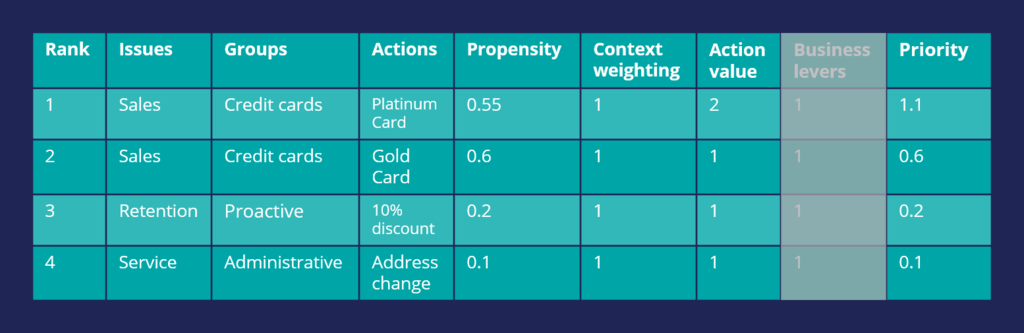
Consider another scenario in which a customer is eligible for two credit cards and two other actions. Now, consider that the Action Value is also used in arbitration when prioritizing. In this case, the Platinum Card is assigned a higher value by the business than the Gold Card.
Thus, the arbitration selects the Platinum Card as the top action.
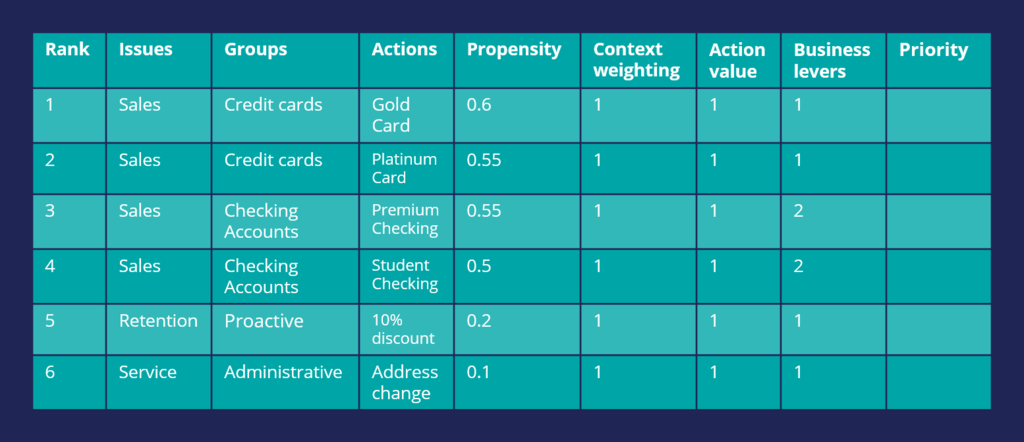
Finally, consider an example in which all four parameters are used for arbitration. In this case, U+ Bank wants to promote two new checking account offers under the Sales issue. The bank sets a higher Business Lever value for the Checking Accounts actions.
Although the Propensity of the Checking Accounts actions is low, they are selected as the top actions due to their high Lever values.
This Topic is available in the following Modules:
If you are having problems with your training, please review the Pega Academy Support FAQs.
Want to help us improve this content?