Basics of routing work for designers
Routing work
When there is more than one operator to complete work on a case, you define who should do the work on each assignment as you model a process. Careful and appropriate assignment routing design increases business efficiency because assignments go to the individual or group of individuals most capable of completing a specific assignment.
For example, when creating an expense report, an employee creates the report, a manager approves it, and payroll sends the money — three roles, either an individual or a team, are working on the same case to fulfill their part of the assigned work.
Check your knowledge with the following interaction.
Routing types
You use assignment routing to assign work to the most appropriate user. You can route a step to a single user or to a team of users.
A worklist (known as a tasklist in the Pega Cosmos design system) is a list of all open assignments, in order of importance, for a specific user. For example, a task requires a human resources manager to approve employee time off requests routes to the worklist of the human resources manager.
A work queue is a list of all open assignments, in order of importance, for a group of users. Assignments stay in the work queue until a user associated with the work queue selects an assignment, or a manager sends an assignment in the work queue to a specific user.
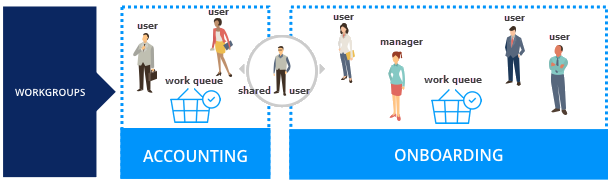
A work group identifies a cross-functional team that contains a manager, users (operators), and a work queue. You create work groups to share resources across the business. For example, the following team contains members from different parts of the organization and in different roles.
Pega refers to work groups as teams and operators as team members.
Check your knowledge with the following interaction.
This Topic is available in the following Module:
If you are having problems with your training, please review the Pega Academy Support FAQs.
Want to help us improve this content?
